Pengcheng Ding

I am currently getting my PhD from Johns Hopkins University. My research area is electricity market. I build game theory based optimization models to simulate how different market players respond to different policies and market prices for policy recommendation.
Extracting insights from mathematical models for real-world decision making has been passion for the past few years. I believe data science is the field where I can combine my skills and my passion to help inform better decisions. This belief has driven to join the Insight program as an Insight Fellow, where I furthered my understanding of machine learning and helped a company to develop its first keyphrase extraction pipeline. This experience has solidified my understanding of machine learning and made me determined to seek a career as a Data Scientist.
View My Resume
View My LinkedIn Profile
Portfolio
Bi-LSTM-CRF Keyphrase Extractor
Summary
As an Insight Fellow, I built the database and model for a healthcare communication company to store and extract keyphrases from the abstracts of scientific literature on PubMed. The company needs a database of certain PubMed records annotated with keyphrases. However, less than 26% of the records come with author provided keyphrases. To make use of the existing author annotated keyphrases and the future company annotated keyphrases, I built a supervised learning model that was trained on these existing records to extract keyphrases from the literature abstracts. Finally, to help the company better filter and index these records with their keyphrases, I built Elasticsearch database with Kibana and clio-lite powered frontend for easy web query and visualization.
Some technical details
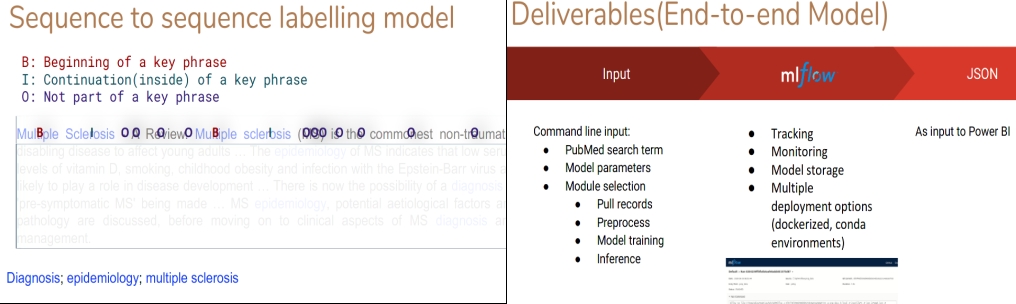
I first started with traditional unsupervised keyphrase extraction models like TF-IDF and TextRank, however, their performances are not good enough for the company. I then built the keyphrase extraction model as a sequence tagging model and used Bi-LSTM neural net architecture, which achieved much better performance. By adding a Conditional Random Field model that takes the LSTM output to calculate its emission score and builds relationship among adjacent predicted labels, the model performance was further improved. Noticing that the many out of vocabulary keyphrases not tagged by the model, I switched to use BioWordVec which includes sub-word embeddings and was trained on the PubMed database to further improve model performance.
The model was fully modularized and implemented into the MlFlow framework to allow for monitoring, results and model storage, and easy deployment.
Results and more
Final models yields a 53.5% F1 score, which is not too far from the current state of the art result achieved on the test dataset. The company has moved some of the visualization work flow from Power BI to Kibana in preparation to replace that with their own platform.
Presentation slides can be found here. Repo for the code is here.
HackerNews Topic Modeling and Auto-encoder based Recommendation Engine
Summary
In this project, I propose a new kind of recommendation engine that aims to find news post that is different from most other posts under similar topic. The news source I use is Hacker News, a social news website focusing on computer science and entrepreneurship. Users of the website can submit news post (usually with some external link) to the website for others to see, upvote and comment. However, Hacker News does not provide a topic categorization system (only posts concerning job posting, showcasing one’s own work and questions to the community are categorized). With more than 500 posts every day, it has become hard to find posts that should interest you.
The project contains two part. In the first part, I build a topic categorization system based on post title, content and linked url. The second part is an autoencoder based model to find posts in each topic groups that stand out. These stand out posts are considered different from most of the other posts under the same topic. They might be about new ideas or tools that are not well accepted yet (they may be rough around the edges, but may have strong potential to change the status quo). And due to this, they may receive few upvotes from other users and are thus more difficult to find.
Some technical details
I’ve obtained around 2 Million HackerNews posts from Google’s BigQuery platform. First model I tried for the topic modeling is the LDA model with processed texts. However, since each entry/document in the input (the combined texts of post title, content, and link domain) contain only few words, LDA, which relies co-occurrence of words to determine topic distributions, do not work well on these short text classification tasks. Pre-trained language models like BERT can generate contextualized sentence embeddings which provides numerical representation of the sentence which encompasses semantic relationships between the represented sentence and the corpus (Wikipedia+BookCorpus) BERT trained on. We can use these representations for an unsupervised clustering model for topic modeling.
To possibly improve topic modeling performance, I concatenated the LDA output(topic distributions for each post) with the Distilled-BERT embeddings, used auto-encoder for dimensionality reduction and finally clustered the results into different topics. The main justification is that certain topics naturally associate with certain jargon and LDA contain this information by modeling word co-occurrence. I then run TF-IDF to get the key words of these topics. Another way to get key words is to find the words with embeddings that have large cosine similarity to the topic embeddings (averaged sentence embeddings), which is much more time consuming.
In the second part of the project, I try to find the unusual posts for recommendation using an auto-encoder model for each topic. The auto-encoder takes the posts embeddings as input, reduce them to smaller dimensions, and then reconstruct the posts embeddings from these smaller dimension representations. The unusual posts are defined as posts that are harder to reconstruct with the decoders of auto-encoders, which suggest that they differ from other posts in this topic. I have tested using both sentence level embedding (in a neural network with all dense layers) and word level embeddings (in a neural network utilizing LSTM or CNN structures) as the auto-encoder input. The results are much better using word level embeddings. Another observation is that auto-encoders could also filter out lower quality posts (like advertisements), to further improve model performance, an auto-encode should be built on the whole dataset, and filter out these posts before doing topic modeling and recommendation. Also, LSTM and CNN auto-encoders perform similarly on this task, although CNN ones paralleled much better are faster to run.
Repo for this project is hosted here